
In today’s society, many of the millennial condo buyers use the internet websites to gather information and make comparisons on which condo they would like to purchase. However, it can be complicated and struggling for new users who are using their website as they need to input and consider a variety of factors before they proceed to search for their desired condo. I came along with an idea to create a suggestion map to use Google Maps to search for the condominium suite to meet the user’s demands.
Data Scraping:

My first task in this project is to collect the data from a condominium website called Condos.ca to extract all the necessary information to create a map. I am using a Python package called BeautifulSoup in order to parse HTML pages from the website. I have collected the data from each individual regions in the GTA area, which the user is given an option to input the minimum and maximum price as well as the region they are looking for. Other processes required to do this is making functions to check the next condo posting within the list and checking if the next page exists at the end of the page. I will store all the information I collect to dictionaries and append them to a list to import them into a data frame.
Data Cleaning:
My next step is to clean the data, so the format is organized and easy to read. Cleaning data involves putting the dollar signs in front of price columns, filling in the missing value and removing the features where there is an insufficient information. As shown in the table below, the features that will be included in the marker include area, number of bedrooms, address and price.
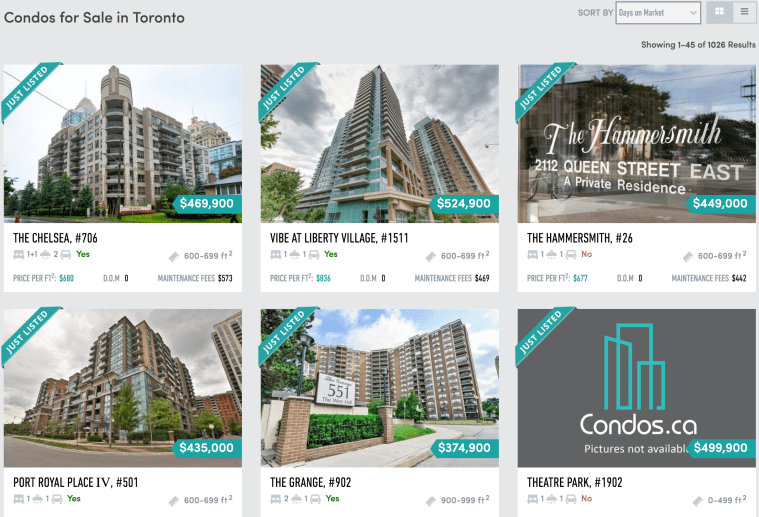

Before moving on to visualizing the data, I need to find out the geographic coordinates in order to plot them. I came across the package called GoogleV3 from geopy.geocoders, which uses Google API to convert the following addresses to geocoders. Then, I will save the latitudes and longitudes to nested lists for later use.

Data Visualization:
Now let’s move on to what type of maps we want to make. The maps I thought were interesting that I decided to do are heatmap and marker map.
The heat map will point out the condo suites that have not been sold for a long time to determine the areas that the users would like to avoid when they are looking for their condo.

To find this out, I need to differentiate the condos that have been on the market up to 20 days, between 21 to 40 days and over 40 days. I am using for-loop to assign colors to each section and plotting them on to a pie chart using the library called matplotlib. There is a higher percentage of condos that have been on market for less than 21 days, whereas there are fewer condos that have not been sold for over 40 days.
Furthermore, using Google API using gmaps library, I am able to plot the coordinates according to the list of old condos that I have gathered. The center point coordinate will be the first location within the list.
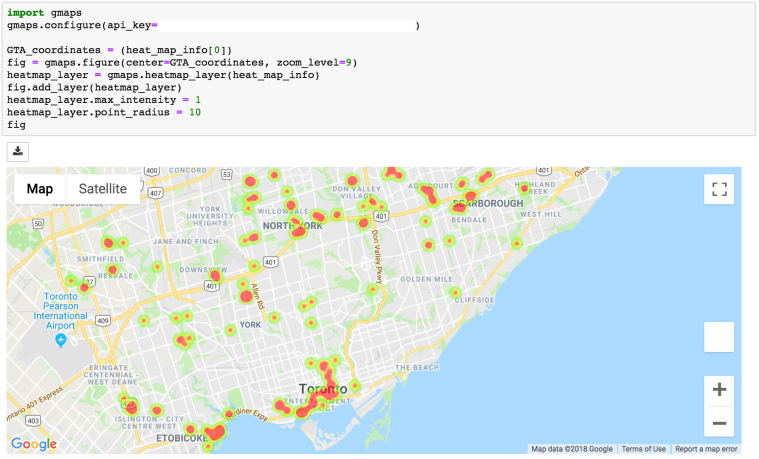
The disadvantage of using a heat map is that it does not function very well in a crowded area as it can highlight some of the important areas where there is a combination of condos that are new and old. In this case, you can zoom in to specific areas to find out which specific condos that are highlighted. The heat map is generally more efficient when the region is not too correlated and where it is easier to determine which condos are relatively older.
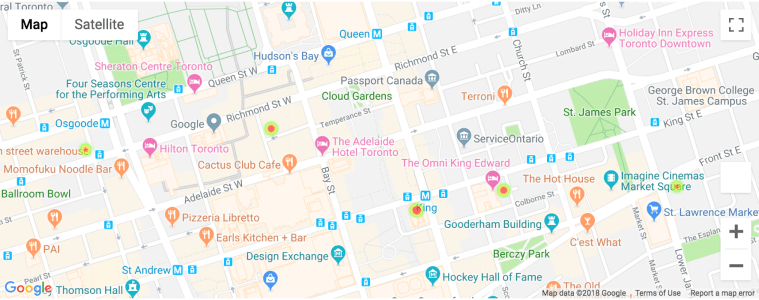

To overcome the cons of the heatmap, I had to come up with another map that can actually plot out the details information of condos. Before moving on, I want to find out the quantity of each number of bedrooms available on the market. I found out that there are more of 1 bed, 1 + den and 2 bedrooms available.
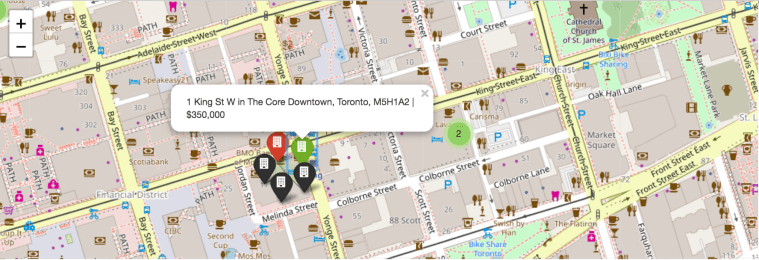
The first marker map is using gmaps, which is the same library I have used for the heat map. The content of the box can be either plain text or HTML format. I have used HTML format to label my marker into the style that is shown below. The marker within the map will have red circle dots for all the list of condos within the dataset. Once you click them, it will show the information on condo address, number of bedrooms and condo price.

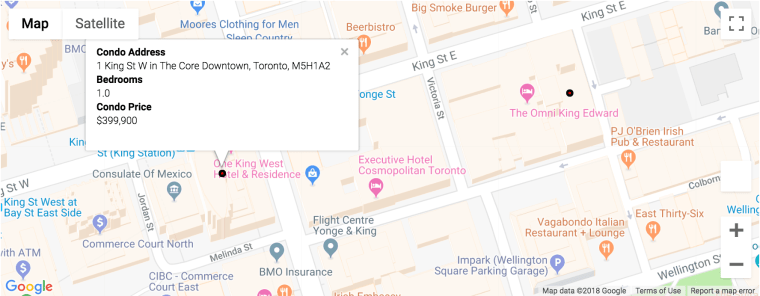
Although the marker map using gmaps library has a better visualization and neater formatting for the marker itself, it lacks in speed when comparing to the map using the Folium package. Folium package is another library that can be used to provide markers. Even though it lacks in visualization, it does have higher speed and can add colors for markers to differentiate the condos based on the days on market. I have made the differences based on the pie graph shown before. The green marker being days on market less than 21 days, the red marker being days on market between 21 days to 40 days and black marker being days on market over 40 days.
Conclusion:
In short, I have demonstrated an example of a web scraping project that uses BeautifulSoup package to parse the HTML data from online and visualize the sources on to numerous useful maps.
My next step is gathering more data to apply machine learning algorithms and create a useful user friendly analytical website.
Thank you!
∞




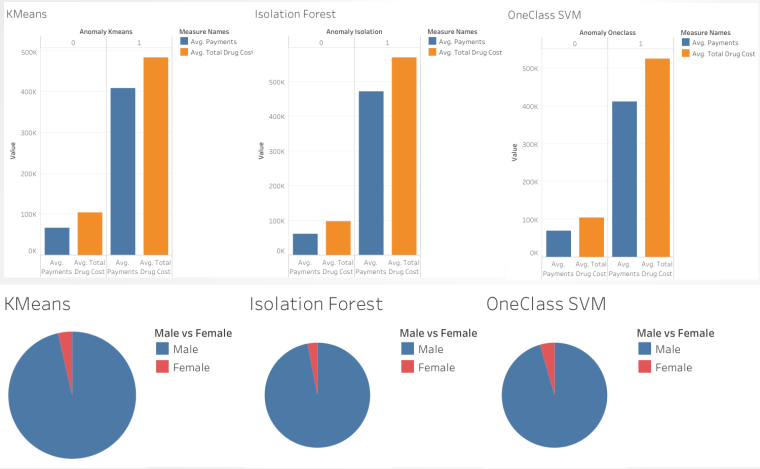

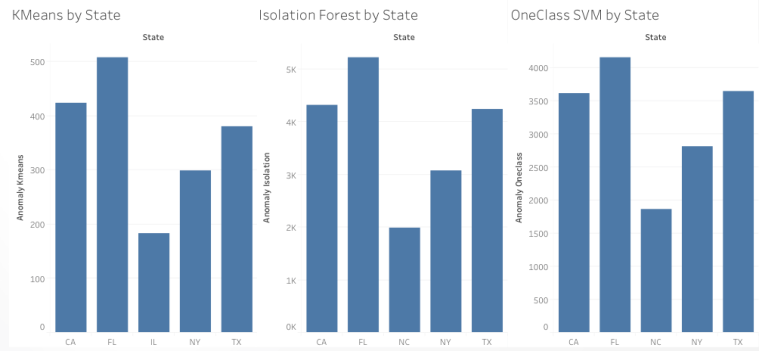




 Top 5 features according to the graphs are loan_payment, maximum_trans_balance, issuance_after_transaction, and loan_amount. As you can see in the bar graph, the maximum transaction balance is higher and the minimum transaction balance is lower for the clients who are defaulted.
Top 5 features according to the graphs are loan_payment, maximum_trans_balance, issuance_after_transaction, and loan_amount. As you can see in the bar graph, the maximum transaction balance is higher and the minimum transaction balance is lower for the clients who are defaulted.